normal end tidal co2 pediatric
Many neonatal intensive care units NICU have converted to utilizing transcutaneous CO 2 tcP CO2 monitoring. This non-invasive approach has promise but as of now has not proven to be an effective tool in determining the degree of dehydration in children.
Respiratory Monitoring Department Of Pediatrics Uw Madison
However et CO 2 may be underused in the PED setting.

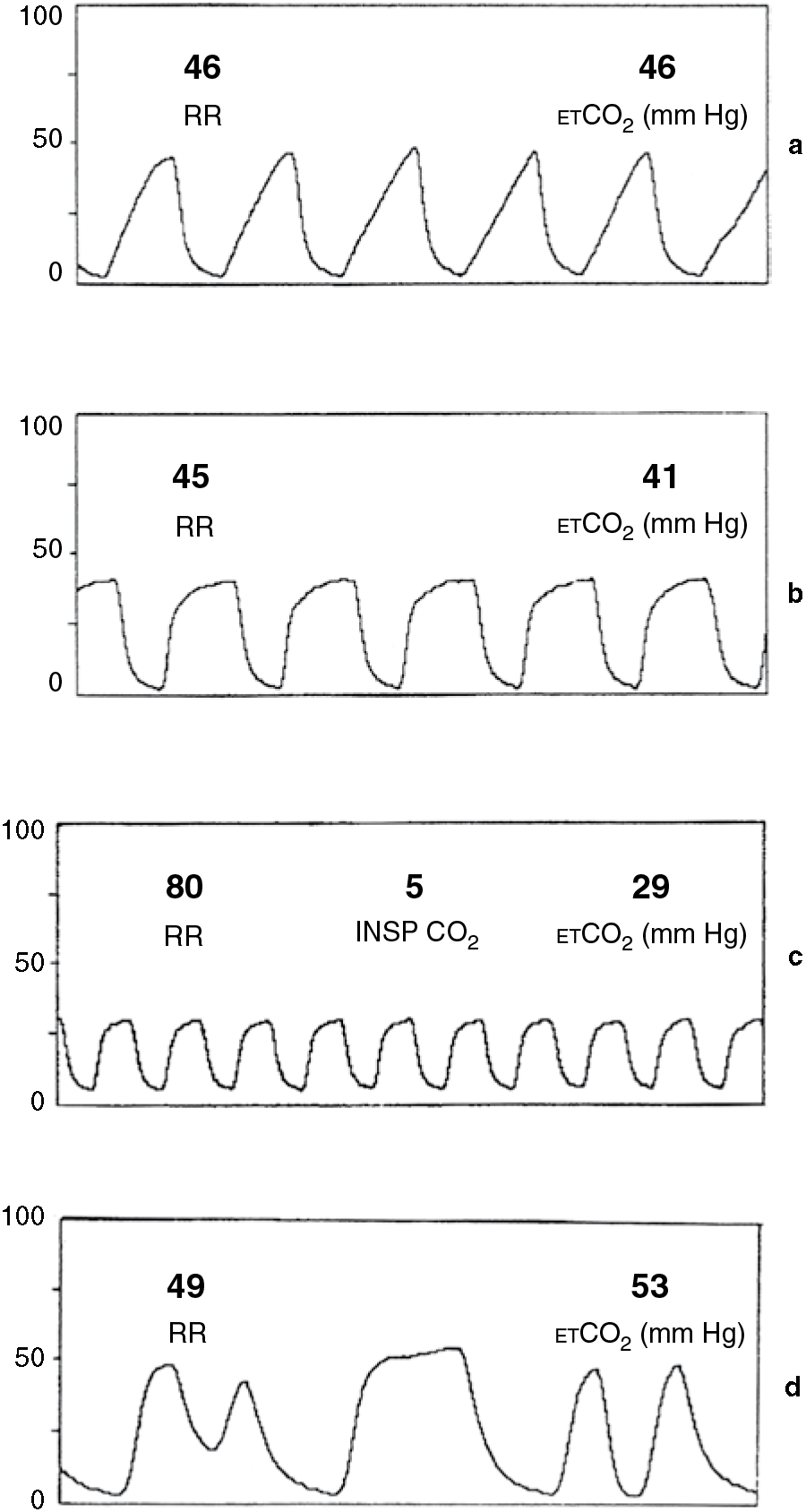
. The amount of CO2 at the end of exhalation or end-tidal CO2 ETCO2 is normally 35-45 mm HG. End-tidal CO 2 et CO 2 monitoring is not a new modality in the pediatric emergency department PED and emergency department. Poor signal in mouth-breathing patients.
To identify the role of end-tidal carbon dioxide EtCO2 monitoring during polysomnography in evaluation of children with obstructive. Normal ETCO2 is 35-45 mm HG and a normal waveform is rectangular shaped. 24 Casti A Gallioli G Scandroglio M Passaretta R Borghi B Torri G.
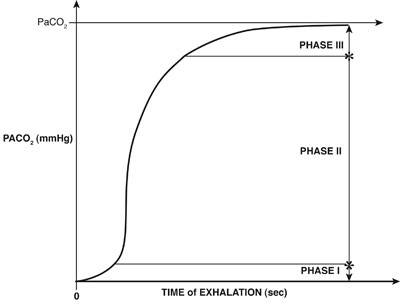
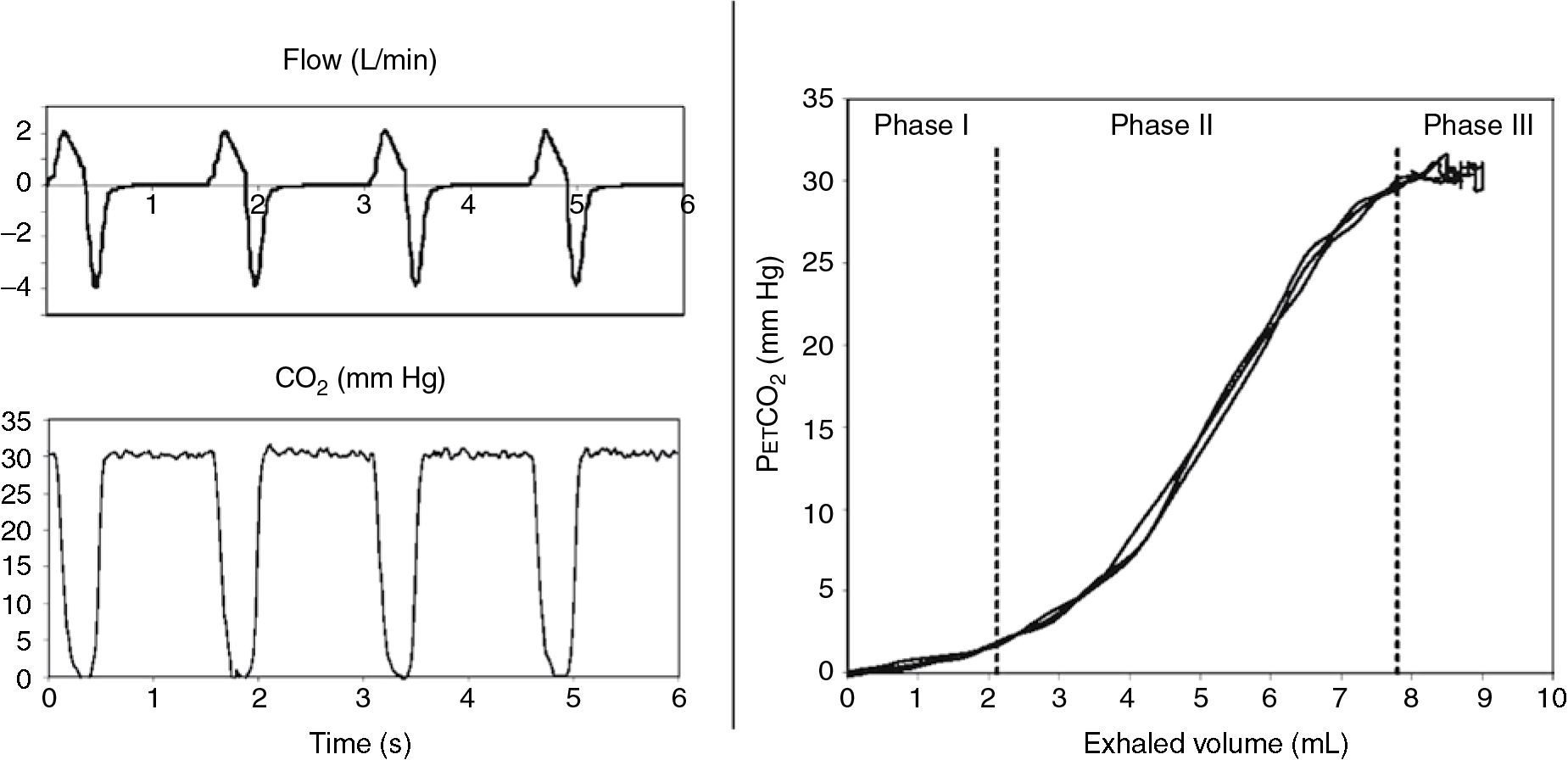
For a person with normal lungs the difference between end tidal and Paco2 can vary between 5-8mmHg depending on the book your reading. Frequently obstructed by secretions etc. With a normal match of alveolar ventilation and perfusion this gradient is roughly 2 to 5 mmHg where the arterial carbon dioxide is greater than the exhaled carbon dioxide.
Provides a quantitative assessment of the PCO 2. Evaluation of a mainstream capnometer and end-tidal carbon dioxide monitoring in mechanically ventilated infants. End-tidal carbon dioxide measurements have been studied in an attempt to assess degrees of dehydration greater than five percent in children.
35-40 mm Hg PETCO2 less than 10 indicates ineffective chest compressions. Continuous Waveform Capnograpy is written as PETCO2 which stands for patient end-tidal carbon dioxide. Prior to the reading the monitor was left in place for approximately 5 minutes at which time an arterial blood gas value was obtained.
Of normal lung parenchyma. It is known to be less accurate in the infant population than in adults. End-tidal CO2 monitoring is an exciting non-invasive technology that is more commonly used in the emergency department intensive care unit and in the prehospital setting.
May be over-sensitive in detecting airflow. End-tidal CO 2 Et CO2 is the standard in operative care along with pulse oximetry for ventilation assessment. 22-26 mEqL O2.
Under normal conditions the end tidal CO2 is usually slightly less than the PaCO2 with a normal difference of 25 mmHg. Use as a quantitative measure of PCO 2 rather than a primary measure of airflow. The mean difference between the transcutaneous and arterial CO 2 value was 194 mmHg with a 95 confidence interval of 012 to 407 mmHg.
In normal healthy lungs the match of arterial carbon dioxide and exhaled CO 2 is closely correlated. These values are consistent across all age groups. In summary hypoxemia is a serious problem in the sedation of pediatric dental patients and none of the time-honored methods of monitoring these patients is reliable as a warning of hypoxemia.
Mean ETCO2 20 mmHg during pediatric in-hospital CPR was not associated with survival to hospital discharge and ETCO2 was not different in survivors versus non-survivors. The normal value for PaO2 when breathing room air is 90- 100 mm Hg. When a person is breathing in it.
1-3 Clinicians may however observe a widened or increased gradient caused by physiologic dead. Compensated shock can be detected by evaluating the patients. 2 See Figure 1 p.
Note that this gradient may be considerably higher in situations where there is an increase in dead space. The PaCO 2 value varied from 19 to 86 mmHg. For oxygenation adjust FiO2 PEEP inspiratory time PIPtidal volume increase MAP.
Respiratory inductance plethysmography sum signal. So the short answer is you are right about the ranges 35-45 but that is for actual PaCo2 drawn from an ABG. End-tidal carbon dioxide during pediatric in-hospital cardiopulmonary resuscitation.
95-100 on room air BE - 1 Lowest acceptable SBP for patients older than 1 yr 70 2 x age in years Cardiac arrest in the pediatric patient is also commonly due to progressive shock. End-Tidal Carbon Dioxide during Pediatric PSG. The technique has been End-tidal carbon dioxide monitoring in neonates Carbon dioxide monitoring is vital in the management of ventilated newborn babies.
As stated before end tidal is slightly different. Adverse driving behaviors are associated with sleep apnea severity and age in cognitively normal older. During sedation capnography is often used to assess the breath-to-breath analysis of carbon dioxide concentration.
48 When a person is breathing out CO 2 the graph goes up. Each patient was monitored until a reliable 5-minute ETCO2 waveform was obtained. Do not make more than 2 alterations at any one time.
23 Meredith KS Monaco FJ. Its main use has been in verifying endotracheal tube position during mechanical ventilation and cardiopulmonary resuscitation but it is being studied and used for other purposes as well. Carbon dioxide is produced in the body as a by-product of metabolism and is eliminated by exhaling.
End-tidal carbon dioxide monitoring or capnography End-tidal carbon dioxide EtCO 2 monitoring is an attractive method as it is non-invasive portable and relatively inexpensive. The normal end-tidal capnography wave form is basically a rounded rectangle. Accuracy of end-tidal carbon dioxide monitoring using the NBP-75 microstream capnometer.
It is the standard of care during certain procedures such as intubations and sedations and can be used in variety of clinical situations. 0 Comments Comments 0. This study was designed to determine whether end-tidal carbon dioxide ETCO2 values obtained by noninvasive oralnasal cannula circuit with side-stream capnometry correlate reliably with capillary PCO2 CapCO2 in a pediatric population without cardiopulmonary problems.
Maintanence of Ventilation- Fine tuning after initiation is based on blood gases and oxygen saturations.

Capnography In The Pediatric Emergency Department Clinical Applications

Pdf Capnography For Monitoring End Tidal Co2 In Hospital And Pre Hospital Settings A Health Technology Assessment Semantic Scholar
Neonatal Monitoring Chapter 10 Capnography

Continuous Capnography In Pediatric Intensive Care Semantic Scholar

Continuous Capnography In Pediatric Intensive Care Semantic Scholar

Etco2 Valuable Vital Sign To Assess Perfusion The Airway Jedi

Pdf Applications Of End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Etco2 Monitoring In Emergency Department A Narrative Review Semantic Scholar

Carbon Dioxide Monitoring In Children A Narrative Review Of Physiology Value And Pitfalls In Clinical Practice Humphreys 2021 Pediatric Anesthesia Wiley Online Library

Pdf Capnography In Pediatric Critical Care Unit And Correlation Of End Tidal And Arterial Carbon Dioxide In Ventilated Children

Exhaled End Tidal Carbon Dioxide As A Predictor Of Lactate And Pediatric Sepsis The American Journal Of Emergency Medicine

Pdf Capnography In Pediatric Critical Care Unit And Correlation Of End Tidal And Arterial Carbon Dioxide In Ventilated Children
Arterial And End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Difference In Pediatric Intensive Care Topic Of Research Paper In Medical Engineering Download Scholarly Article Pdf And Read For Free On Cyberleninka Open Science Hub

Association Between Etco2 And Paco2 In Infants And Children Download Scientific Diagram

The Impact Of Ventilation Rate On End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Level During Manual Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Resuscitation

Pdf Capnography In The Pediatric Emergency Department Clinical Applications Semantic Scholar

End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Recording Of Ventilated Children In Picu N 535 Download Scientific Diagram

Continuous Capnography In Pediatric Intensive Care Semantic Scholar